Simple SEO Tutorial
Tutorial Goal
The aim of this tutorial is simple: follow the steps, and you'll achieve 80% of your website's SEO potential. You don't need to understand the "why" or even what SEO is – just follow the instructions.
Therefore, this tutorial will not delve into "what is SEO" or the theoretical aspects. It focuses solely on "how to do SEO" effectively.
If you're looking for explanations on "what is SEO" or "how does SEO work," I recommend checking out the original tutorial here: Tutorial Source.
If you're after practical guidance on "how to do SEO," this tutorial is perfect for you.
This tutorial is 90% distilled from the Ahrefs SEO tutorial. Think of it as a concentrated version of the original.
You can find the full Ahrefs SEO tutorial here: https://ahrefs.com/blog/zh/how-do-search-engines-work/. Take a look when you have the time.
If you're ready, let's begin!
The Quick Start Guide: Implementable in 10 Minutes
0. Ensure Your Website is Static or Server-Side Rendered
Many beginners overlook this, only to find their SEO efforts are ineffective.
Why?
Search engine crawlers (like Googlebot) can directly read HTML content from static or server-side rendered pages. This makes it much easier for them to crawl and understand your website.
Websites that rely on JavaScript to generate content within the browser (client-side rendering) require crawlers to spend more time, and there's no guarantee Google will even execute the JavaScript. This impacts indexing and ranking.
Also, static or server-side rendered pages typically load faster, providing a better user experience—something Google values highly.
Consider using frameworks like Next.js or Nuxt.js. They handle many SEO aspects for you.
1. Keyword Research
- Brainstorm words related to your business/website (e.g., for an SEO tutorial site, consider "SEO," "keyword research," "on-page optimization," etc.).
- Use keyword research tools (like Ahrefs' Free Keyword Generator, Google Keyword Planner, Semrush, etc.) to find more related terms.
- Jot down the most promising keywords.
- Use GPT to help you find even more keywords.
Key Considerations for Keyword Selection:
- Relevance: Keywords must be relevant to your business/website.
- Traffic Potential: Keywords should have the potential to drive traffic.
- Search Volume: Target keywords with reasonable search volume, avoiding overly niche terms.
- Keyword Difficulty (KD): Aim for lower KD scores (available in keyword research tools). Lower KD indicates less competition and easier ranking.
2. Content Creation
- Analyze Competitors: Google your target keywords and analyze what's working for the top-ranking content (type, format, angle).
- Match Search Intent: Fulfill the information needs of users searching for the keyword (type, format, angle).
- Provide Value: Share genuine experience, solve user problems, and demonstrate expertise.
- Be Comprehensive: Cover all relevant aspects users might want to know, aiming for more thoroughness than competitors.
- Add Unique Insights: Offer unique information or techniques that others haven't covered.
- Ensure Readability: Use short sentences, paragraph breaks, and images. Proofread for typos.
- Keep Content Updated: Regularly update outdated information.
3. On-Page Optimization
- Meta Tags & Titles:
- Page Title (Title Tag): Compelling, includes keywords, and has an optimal length (around 60 characters). (Example:
<title>The Ultimate Guide to On-Page SEO (2024)</title>) - H1 Tag: Use one H1 tag per page to summarize the page topic. (Example:
<h1>The Ultimate Guide to On-Page SEO</h1>) - H2-H6 Tags: Use for subheadings to organize content structure.
- Meta Description: Describes page content, attracts clicks, includes keywords, and has an optimal length (around 150-160 characters). (Example:
<meta name="description" content="Learn everything about on-page SEO, from keyword optimization to technical details, to boost your website ranking!">)
- Page Title (Title Tag): Compelling, includes keywords, and has an optimal length (around 60 characters). (Example:
- Links:
- Internal Links: Link to other relevant pages on your website, ideally creating a pyramid structure. Avoid orphaned pages that Google can't find. (Example:
<a href="/keyword-research">Learn Keyword Research</a>) - External Links: (If necessary) Link to authoritative sources or useful external resources. (Example:
<a href="https://example.com" rel="nofollow">Reference Material</a>)
- Internal Links: Link to other relevant pages on your website, ideally creating a pyramid structure. Avoid orphaned pages that Google can't find. (Example:
- Images:
- Filename: Use descriptive filenames. (Example:
on-page-seo-checklist.jpg) - Alt Text: Add descriptive alt text that describes the image content. (Example:
<img src="..." alt="Screenshot of an on-page SEO checklist">) - Compression: Compress image file sizes to improve loading speed.
- Filename: Use descriptive filenames. (Example:
- URL Structure:
- Concise & Descriptive: URLs should be short, easy to understand, and ideally include keywords (use
-to separate words). (Example:/on-page-seo-guide/)
- Concise & Descriptive: URLs should be short, easy to understand, and ideally include keywords (use
- User Experience:
- Page Speed (Core Web Vitals): Optimize loading speed.
- Mobile-Friendliness: Ensure a good mobile experience.
- HTTPS: Use HTTPS encryption.
- Avoid Intrusive Pop-ups: Minimize distracting advertising.
- (Optional) Featured Snippet Optimization: Provide concise answers to specific questions.
- (Optional) Schema Markup: Add structured data to help Google understand your content.
4. Building Backlinks (External Links)
- Create Exceptional Content: Focus on creating content that is exceptionally useful and valuable, making others want to link to your articles or recommend your tools (this is the most crucial and sustainable approach).
- Submit to Directories: Submit your website to a few of the most important and authoritative industry directories (e.g., industry-specific resource lists).
- Guest Blogging: If you enjoy writing, consider writing guest blog posts for other websites related to your topic. You can naturally include a link to your website in the article.
- Avoid Buying Links: Ahrefs strongly advises against buying links. It's extremely risky, can be a waste of money, and could even result in Google penalizing your website.
5. Other Optimizations
- Check Indexing: Use the "URL Inspection" tool in Google Search Console (GSC, free) to ensure Google can find your important pages.
- Fix Broken Links: If you've changed URLs or deleted pages, use Ahrefs Webmaster Tools (AWT, free) to find pages that are now 404s but previously had external links. Redirect them to the new, relevant pages using 301 redirects.
- Adapt to Multiple Languages: If your niche is highly competitive, consider adapting your content to multiple languages. Many websites only compete in English, so translating your content can unlock more traffic.
- Create a Sitemap: Create a
sitemap.xmlfile listing all important pages on your website and submit it to Google Search Console. This helps Google discover your content faster and more comprehensively.- Example (Basic sitemap.xml Structure):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9"> <url> <loc>http://www.example.com/page1.html</loc> <lastmod>2024-01-01</lastmod> <changefreq>monthly</changefreq> <priority>0.8</priority> </url> <url> <loc>http://www.example.com/page2.html</loc> </url> </urlset>
- Example (Basic sitemap.xml Structure):
- Hreflang (Multilingual Tags): If your website has content in multiple languages or targeting different regions, use
hreflangtags to tell Google about the different language/regional versions of each page. This prevents duplicate content issues and ensures the correct version is shown to the right users.- Example (In HTML
<head>):
(Note:<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-us" href="http://www.example.com/en/page.html" /> <link rel="alternate" hreflang="zh-cn" href="http://www.example.com/zh/page.html" /> <link rel="alternate" hreflang="x-default" href="http://www.example.com/page.html" />x-defaultis used to specify the default or non-language-specific version)
- Example (In HTML
- Robots.txt (Crawler Instructions): Place a
robots.txtfile in your website's root directory to instruct search engine crawlers which pages or directories you don't want them to access or index (e.g., admin pages, test pages).- Example (robots.txt Content):
User-agent: * # Applies to all crawlers Disallow: /admin/ # Disallow access to /admin/ directory Disallow: /private.html # Disallow access to /private.html file Allow: /public/ # Explicitly allow access to /public/ directory (if a parent directory is disallowed) User-agent: Googlebot # Applies only to Google crawlers Disallow: /tmp/ # Disallow Google crawlers from accessing /tmp/ directory Sitemap: http://www.example.com/sitemap.xml # Specify Sitemap location
- Example (robots.txt Content):
- Canonical Tags: If your website has multiple pages with identical or very similar content (e.g., URLs with parameters), use
canonicaltags to specify which is the "official" version. This prevents search engines from treating them as duplicate content and diluting their ranking potential.- Example (In HTML
<head>):
(Note: Even on<link rel="canonical" href="http://www.example.com/product-page" />http://www.example.com/product-page?ref=banner, point to the canonical URL without parameters)
- Example (In HTML
- Schema Markup (Structured Data): Add Schema markup to your page code to explain the meaning of the content to Google in a standardized format (e.g., this is a recipe, a product, an FAQ). This helps Google understand the content and may display richer snippets in search results (like ratings, price ranges, etc.), improving click-through rates.
- Example (JSON-LD Format, placed in a
<script>tag):{ "@context": "https://schema.org", "@type": "FAQPage", "mainEntity": [{ "@type": "Question", "name": "What is SEO?", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is the process of improving the ranking of a website in the organic search results of search engines (like Google) by optimizing its content and technical aspects." } },{ "@type": "Question", "name": "How long does SEO take to show results?", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "The time it takes for SEO to show results varies depending on factors such as website foundation, competition, and resources invested. It typically takes weeks to months or even longer to see significant effects." } }] }
- Example (JSON-LD Format, placed in a
The Detailed Guide
1. Keyword Research
Step 1: Brainstorm "Seed Keywords"
"Seed keywords" are your most basic, core terms. Don't overthink it. Ask yourself:
- How would people search for your products/services online? (e.g., "cheap coffee beans," "how to make pour-over coffee")
- What keywords are your competitors using on their websites?
- If you were a customer, what would you search for?
Example: Let's say you run an online coffee bean store. Your seed keywords might include:
- Coffee beans
- Arabica coffee beans
- Pour-over coffee
- Coffee maker
- Buy coffee beans
Pro Tip:
Stuck for ideas? Ask ChatGPT (or another AI) to brainstorm words related to your business.
List everything that comes to mind—the more, the better.
Step 2: Find More Keywords with Free Tools
Brainstorming isn't enough. Use tools to find more related terms. You don't need to use them all—just pick the ones that suit you.
Tool 1: Ahrefs Free Keyword Generator (Recommended, completely free)
- Go to Ahrefs Free Keyword Generator.
- Enter each of your "seed keywords" one by one.
- Select your target country (e.g., United States).
- Click "Find keywords."
You'll see a list of related keyword suggestions. Focus on these two categories:
- Phrase Match: Phrases that contain your seed keyword. For example, searching for "coffee beans" might show "organic coffee beans" or "best coffee beans."
- Questions: Questions that contain your seed keyword. For example, searching for "pour-over coffee" might show "what tools do I need for pour-over coffee" or "how to make good pour-over coffee."
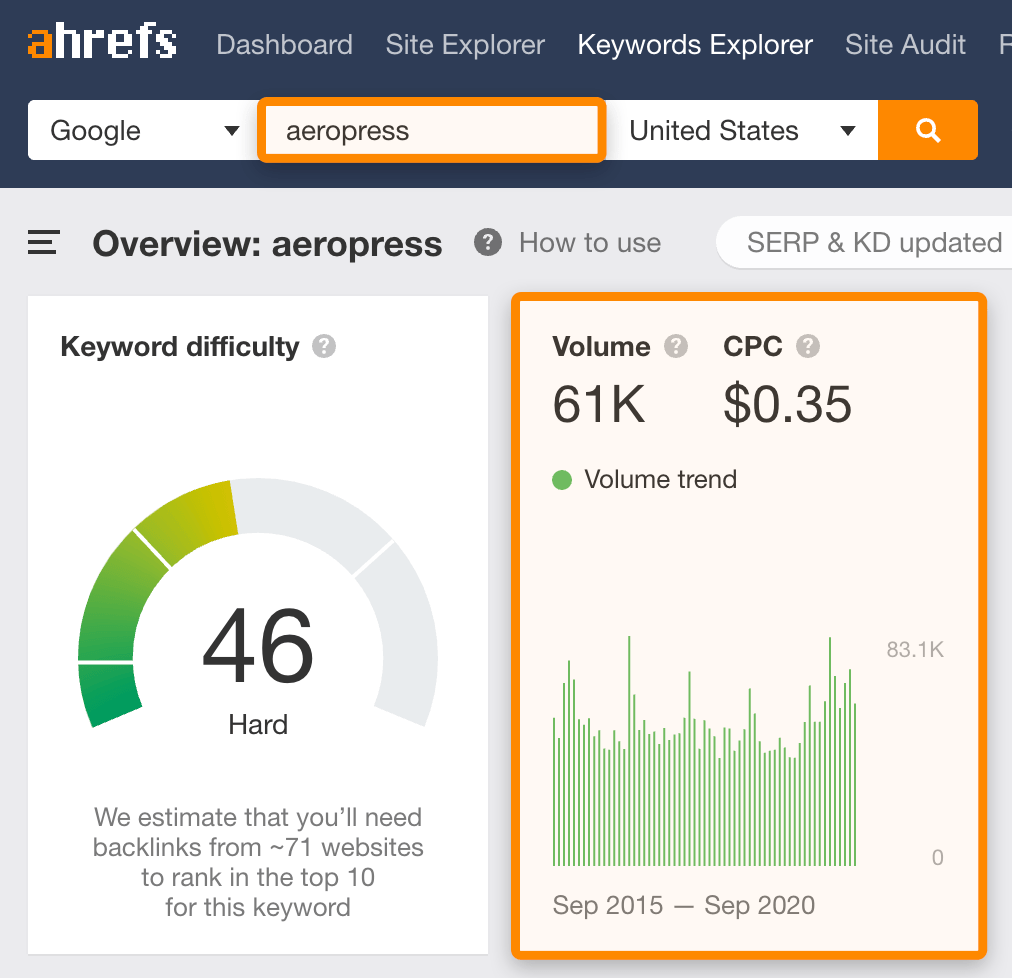
Image Example: Using a keyword tool like Ahrefs to find keywords related to "aeropress" and see their monthly search volume. The free tool interface is similar and will provide a keyword list.
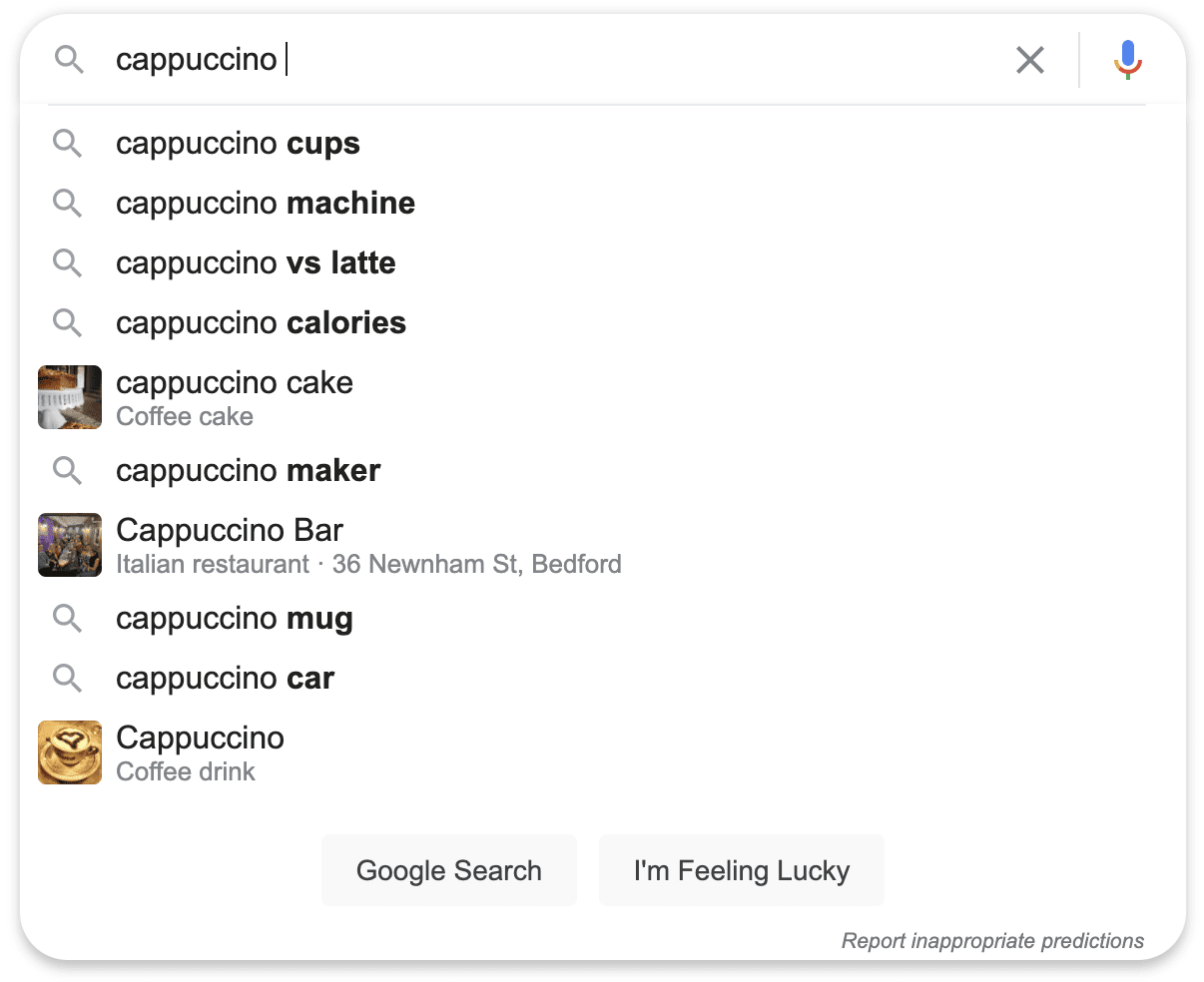
Tool 2: Google Search Box & Related Searches
- Open Google Search.
- Enter your seed keyword and see the suggestions that automatically pop up (Google Suggest). These are popular searches.
- After searching, scroll to the bottom of the page and look at the "Related searches" section. This is another great place to find related terms.
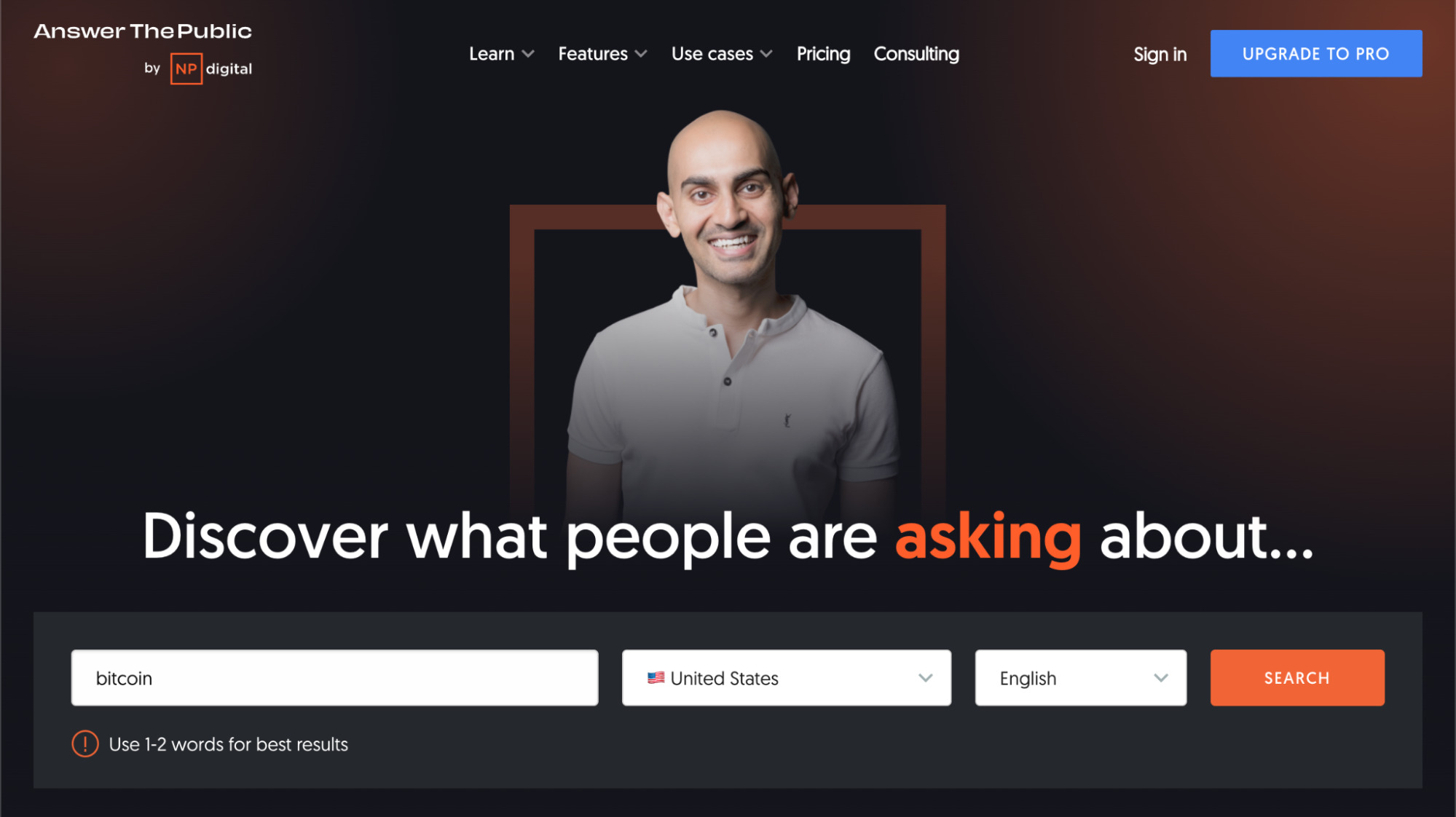
Tool 3: Answer The Public
- Go to Answer The Public.
- Enter your seed keyword (English is recommended for better results).
- Select country/language.
- It will generate a bunch of questions, prepositional phrases, and comparisons related to your keyword, helping you understand what specific questions users are searching for. The free version has daily usage limits.
Tool 4: Google Trends (See Popularity and Trends)
- Go to Google Trends.
- Enter your seed keyword.
- You can see the search interest trend for this keyword and identify seasonal changes or suddenly trending topics.
- You can also see related queries to find other popular terms people are searching for at the same time.
Tool 5: ChatGPT
- Open ChatGPT or another similar AI tool.
- Ask it to generate more related keywords, topics, or questions based on your seed keywords. For example, you can ask, "I sell coffee beans. Please give me some related keywords or questions that people might search for."
Tool 6: Google Keyword Planner (Free, but requires a Google Ads account)
If you have a Google Ads account (you can register for free; you don't need to spend money on ads), you can use Keyword Planner.
- Log in to Google Ads, find "Tools & Settings" -> "Planning" -> "Keyword Planner."
- Select "Discover new keywords."
- Enter your seed keywords.
It will provide search volume estimates and more keyword suggestions. However, the free version shows search volume ranges, which aren't as precise.
Step 3: Browse Forums/Communities/Online Groups/Q&A Sites
- Browse relevant forums/communities/online groups/Q&A sites: If you're in the coffee business, go to coffee enthusiast forums, relevant topics on Quora, and groups on Reddit to see what people are asking, discussing, and using as search terms.
- Check comment sections: The comment sections of your competitors' websites, e-commerce pages for related products, and social media posts can also hide real search terms used by users.
Example: Seeing someone ask "how to make pour-over coffee without a filter" in a coffee forum might be a great keyword you hadn't thought of!
Keyword Research Toolkit
- Toolkit:
- Ahrefs Free Keyword Generator (Main, free)
- Google Search Box & Related Searches (Auxiliary, free)
- Answer The Public (Find questions, free, daily limit)
- Google Trends (See trends, free)
- ChatGPT (AI brainstorm, free)
- Google Keyword Planner (Requires Ads account, free)
- Ahrefs Webmaster Tools: A more powerful free toolset, but you need to verify that you own your website. You can see which keywords your website currently ranks for and discover low-competition keywords, etc.
2. Crafting SEO Content
Step 1: Understand What Users Want to See (Analyze Search Intent)
It's crucial to know what type, format, and angle of content people are looking for when they search for a particular keyword.
- Google your target keyword.
- Look at the top 5-10 results:
- Type: Is it an article? A product page? A video?
- Format: Is it a tutorial? A checklist? A review?
- Angle: Is it "beginner-friendly"? "Cheap"? "Latest"?
- Imitate: Your content type, format, and angle should align with what's already working.
Step 2: Write About What You Know (Demonstrate Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness - E-E-A-T)
Make your content credible and show that you truly understand the subject.
- Write about your personal experiences or areas of expertise.
- Share your experiences and opinions using "I."
- (If applicable) Briefly mention your background or achievements.
Step 3: Be Comprehensive (Cover Everything)
Answer most of the user's questions about the topic.
- Use tools to find related questions/long-tail keywords for the keyword.
- Look at the subheadings in the top-ranking articles and see what points they cover.
- Add the points you find that are important to your content.
Note: Comprehensive doesn't mean verbose. Write according to user intent.
Step 4: Add Something Special (Uniqueness)
Give users a reason to read your article instead of someone else's.
- Share a unique technique, experience summary, or point of view.
- Provide a small resource that others don't have (such as a template or checklist).
- (Advanced) Conduct a small experiment or data sharing.
Step 5: Make Reading Easy (Readability)
Users feel comfortable reading and are willing to continue reading.
- Use short sentences and many paragraph breaks.
- Use subheadings to separate the content.
- Use illustrations to explain or relieve fatigue.
- Use bolding and lists to highlight key points.
Step 6: Keep Content Updated
Avoid declining rankings due to outdated content.
- Check periodically (such as annually): Is the information still accurate? Are the links still valid?
- Update content: Modify outdated information and supplement new content.
- Mark the update date: Let users know that this is the latest information.
3. On-Page SEO
Step 1: Help Search Engines and Users "Understand" Your Page
Match Search Intent.
- Google your keyword and analyze the top 5-10 results. Pay attention to their content type (article/product page/?), content format (tutorial/checklist/review/?), and content angle ("beginner"/"cheap"/"latest"?).
- Your content should align with them, giving users what they want to see.
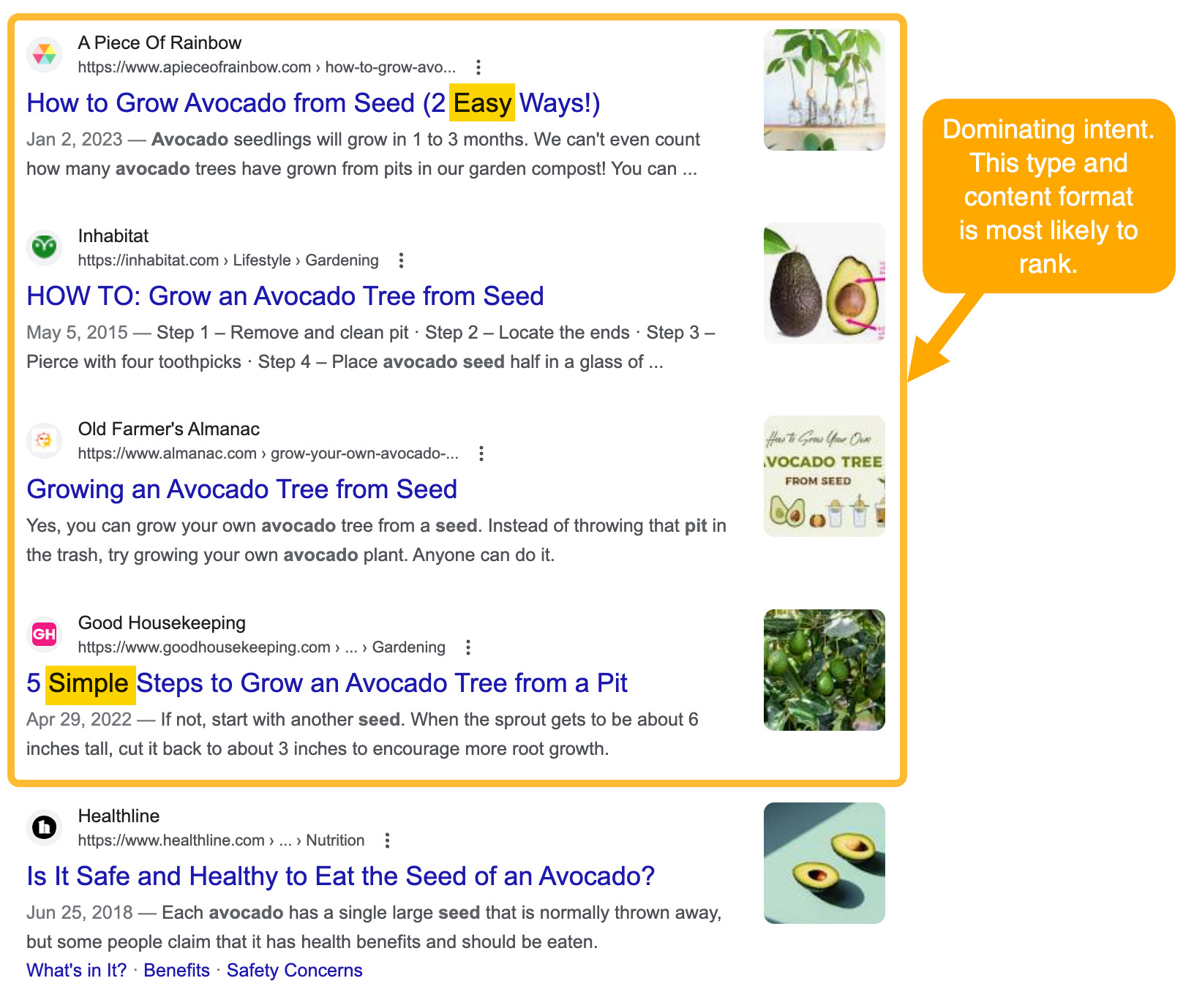
Image example: Searching for "avocado seed" returns mostly guide articles on how to grow them, with the angle being "simple, easy," indicating the user is a beginner.
Write a Good "Headline" (Title Tag):
- Include the core keyword.
- It's best if the length does not exceed 70 characters (about 30 Chinese characters), otherwise it will not be fully displayed.
- Clear and attractive, making people want to click.
- Don't make a pure "clickbait," it must be consistent with the content.
- If the content emphasizes timeliness (such as a tutorial), you can add the year.
- Tool: Let ChatGPT help you brainstorm a few titles. Use Ahrefs Webmaster Tools (AWT)'s Site Audit to check whether the title is too long or missing.
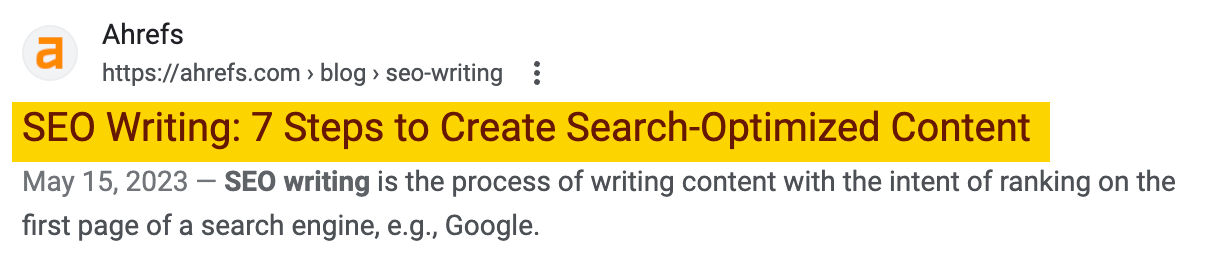
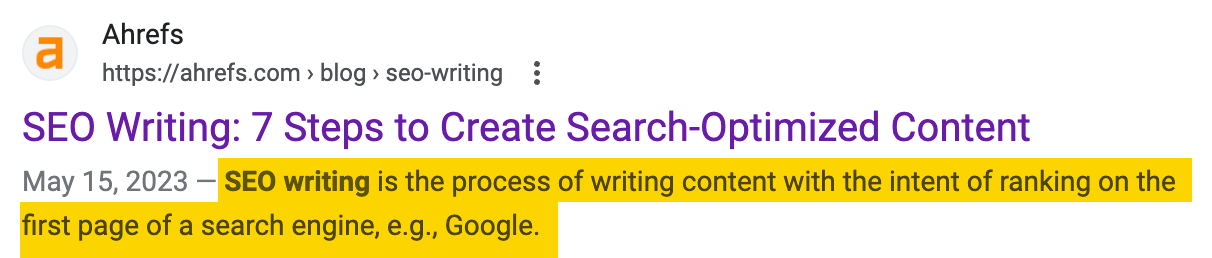
Write a Good "Facade" (Meta Description):
- This is the descriptive text below the title in the search results. Although it does not directly affect the ranking, it affects the click-through rate.
- It's best if the length does not exceed 160 characters (about 80 Chinese characters).
- It can be regarded as a supplement to the title, highlighting some selling points that cannot be put in the title.
- Include keywords (Google will bold them).
- Use active voice and directly tell users what you can provide.
- Tool: Let ChatGPT help you write several versions. Use Ahrefs Webmaster Tools (AWT)'s Site Audit to check whether it is missing or too long.
Create a Good "URL Name" (URL):
- The URL path (the part after the domain name) should be short and easy to understand.
- Include core keywords (use English or pinyin, with
-connecting words).
Image example: domain.com/learn-seo is better than domain.com/p=123
The content should have a "skeleton" (Heading Tags: H1-H6):
- Use H1-H6 tags to organize content and form a clear hierarchical structure to facilitate reading.
- H1 tag: Use only one per page, usually with the same or similar meaning as the page title (Title Tag).
- H2-H6 tags: Used as subheadings for various parts.
- Tool: Use Ahrefs Webmaster Tools (AWT)'s Site Audit to check whether H1 tags are missing or duplicated.
 Image example: Create visual hierarchy using H tags
Image example: Create visual hierarchy using H tags
Step 2: Write "Informative" and "Unique" Content
The content should be "complete":
- Ensure that your content covers the main aspects and questions that users might want to know when searching for this keyword.
- Look at the subheadings (H2, H3) of the top articles in Google search results.
- Look at the "related searches" at the bottom of the Google search results page.
- Tool: (Optional) Use Ahrefs Webmaster Tools (AWT)'s Site Explorer to view which common keywords your website and your competitors' websites bring traffic (Content Gap function), and find subtopics you can supplement.
 Image example: Analyze competitor articles and find that they mentioned "unsubscribe" as a way to save money. Your article can also consider adding this point.
Image example: Analyze competitor articles and find that they mentioned "unsubscribe" as a way to save money. Your article can also consider adding this point.
The content should be "special":
- Don't just repeat what others say, provide some unique value.
- It can be: your unique insights or experience summaries, a small trick that others don't have, an original case analysis, a free template or checklist.
- The goal is to give users a reason to "collect" or "share" your article.
Show your "professionalism" or "experience":
- If you are writing about professional fields (such as medical, finance) or content that requires personal experience (such as product reviews), you must show your professionalism or real experience.
- Clearly state the source of information (quotes, links), provide author background information (link to the author's profile page), share your operating process or usage experience (pictures, videos), and ensure the factual accuracy of the content.
 Image example: Show your actual experience in product reviews.
Image example: Show your actual experience in product reviews.
Step 3: Optimize Details and Enhance Experience
Optimize pictures:
- File name: Name picture files with descriptive words, use
-to separate English words or pinyin (such asblack-puppy-play-ball.jpgorheise-xiaogou-wanqiu.jpg). - Alternative text (Alt Text): This is a picture description for search engines and visually impaired users. Add the
altattribute to the<img>tag in HTML, and use concise language to describe the content of the picture, which can naturally include keywords. (For example:<img src="puppy-playing-ball.jpg" alt="A black Labrador puppy playing with a red ball on the grass">) - Compress pictures: Large pictures load slowly. Use tools to compress the size of the pictures while trying to maintain clarity.
- Tool: Use Ahrefs Webmaster Tools (AWT)'s Site Audit to check whether pictures are missing Alt text. Use online tools such as TinyPNG or iLoveIMG to compress pictures.
 Image example: Good Alt text example
Image example: Good Alt text example
Internal link:
- In your article, link to other relevant articles or pages on your website.
- This helps users discover more content and also helps search engines understand your website structure and page relationships.
- Tool: Use Ahrefs Webmaster Tools (AWT)'s Site Audit's "Internal link opportunities" function to find places where internal links can be added.
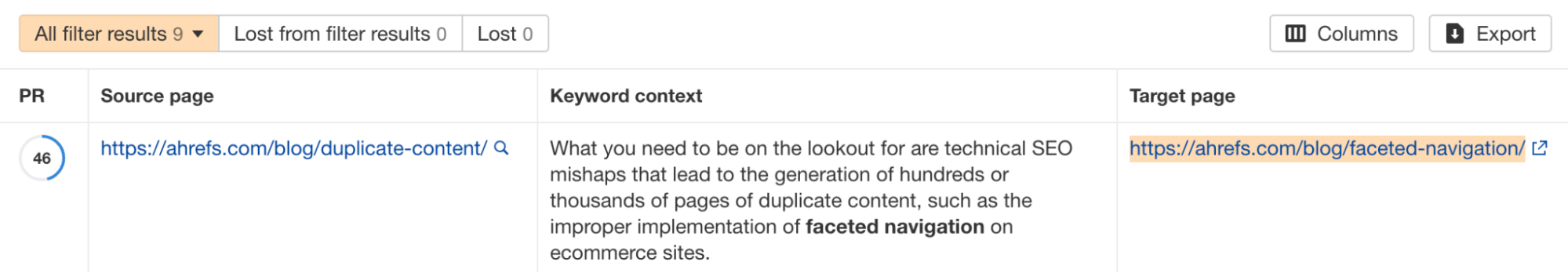 Image example: AWT found internal link opportunities, prompting you to link to page B on page A.
Image example: AWT found internal link opportunities, prompting you to link to page B on page A.
External link:
- In appropriate places, link to other high-quality, relevant external websites as references or sources of information.
- For example, link to the original report when quoting data, and link to the official website when recommending tools.
- Note: If it is an advertising or sponsored link, use the
rel="nofollow"orrel="sponsored"attribute to tell the search engine.
Page Experience:
- Fast loading speed (Core Web Vitals).
- Good browsing experience on mobile phones (Mobile-Friendly).
- Use HTTPS encryption (Security).
- No annoying pop-up ads (No intrusive interstitials).
- These are usually site-wide optimizations, but make sure that new pages also meet the requirements.
- Tool: Use Google PageSpeed Insights to test page speed and experience. View related reports in Google Search Console.
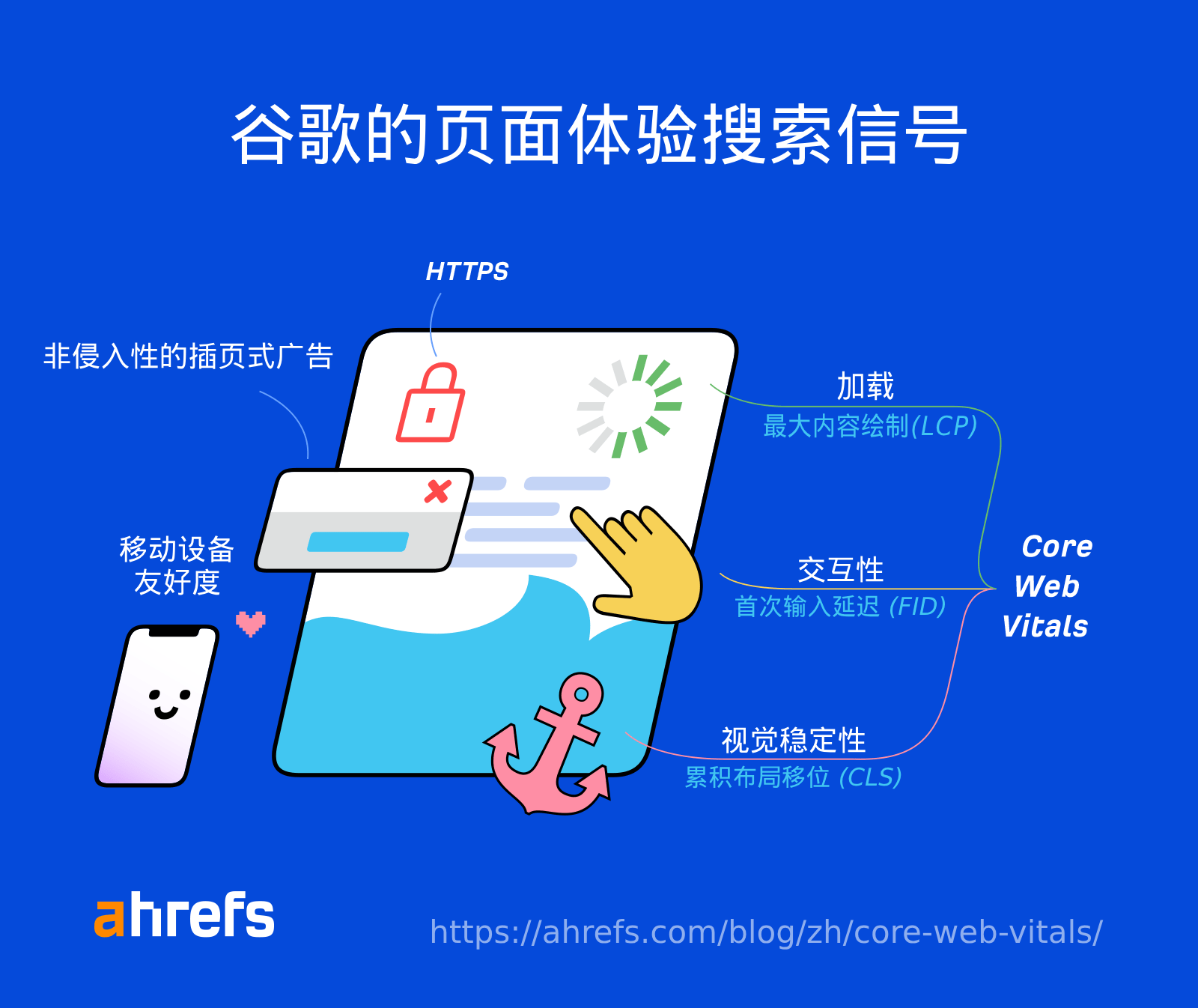 Image example: Google's page experience signals
Image example: Google's page experience signals
Fight for "Special Display":
- Featured Snippet: Google sometimes displays a box that directly answers questions at the top of search results. If your page already ranks in the top few and contains a direct and concise answer to a question in the content (it is best to refer to existing Snippets for the format, such as lists, paragraphs), you have a chance to be selected.
- Rich Snippet: By adding Schema markup (a structured data code) to the page, tell Google what type your content is (such as recipes, FAQs, product information). Sometimes Google will display richer information in search results ( such as ratings, prices, steps).
- Tool: Use Google Search Console to see which keywords you rank high for and Google displays featured snippets. Use Schema.dev's Schema Generator to generate Schema code.
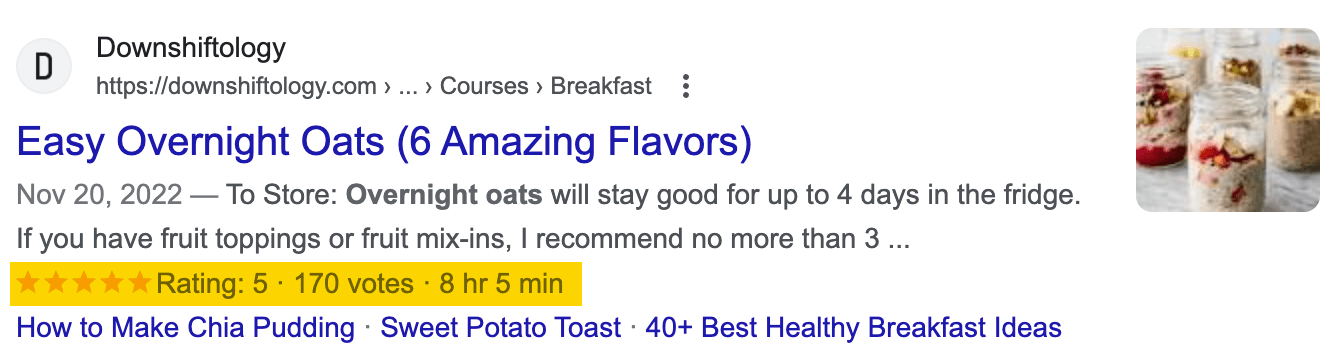 Image example: Rich snippets with ratings and number of reviews
Image example: Rich snippets with ratings and number of reviews
Step 4: Continue to Pay Attention and Update
Monitor effectiveness:
- Pay attention to the ranking changes of your target keywords.
- Use Google Search Console to view the performance of your pages in Google search (impressions, clicks, rankings).
Update content:
- SEO is not a one-time job. Periodically (such as once a year) review your content, check whether the information is outdated, whether the links are invalid, and whether there is new information to supplement. Updating content helps maintain rankings.
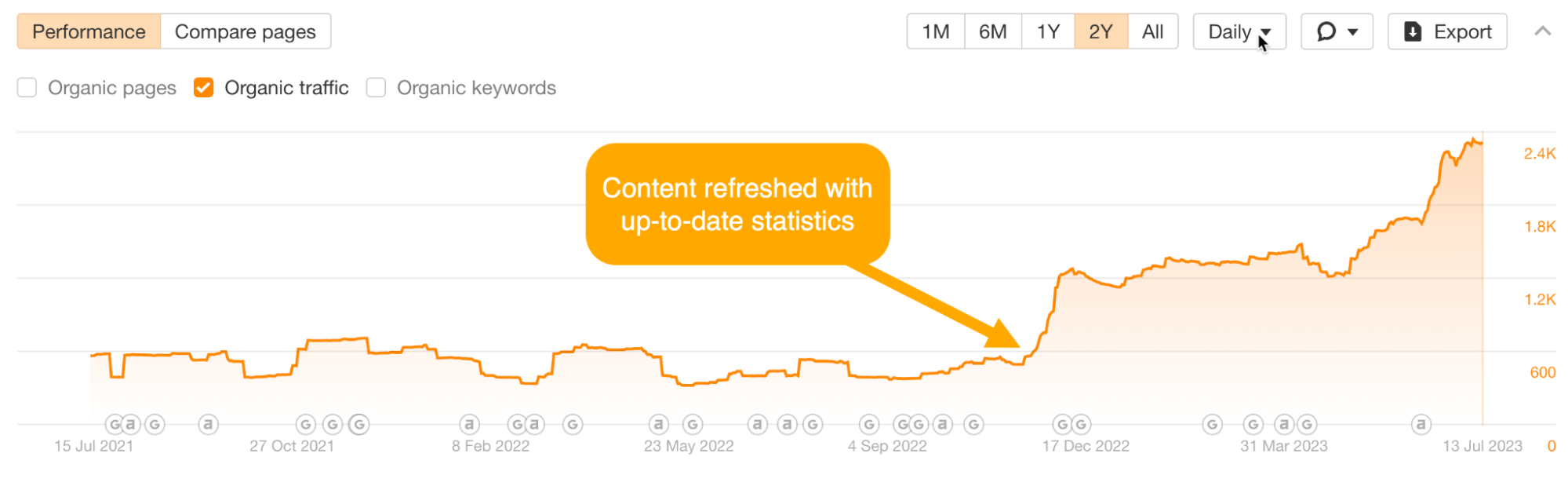 Image example: Traffic growth brought by content updates
Image example: Traffic growth brought by content updates
On-Page SEO Toolkit
- Google Search (Look at intention, look at opponents)
- ChatGPT (Think about title/description ideas)
- Ahrefs Webmaster Tools (AWT) (Free to check H1, title, description, Alt text, find internal link opportunities, see keyword differences)
- TinyPNG / iLoveIMG (Online picture compression)
- Google PageSpeed Insights (Test page speed and experience)
- Google Search Console (Monitor rankings, experience issues, view keywords)
- Schema.dev Schema Generator (Generate Schema code)
4. Building External Links (Backlinks)
What are External Links (Backlinks)?
Imagine the Internet as a vast network of relationships. When another website A places a link on its page that points to your website B, this forms an external link from A to B. Google sees this link as a "recommendation" or "vote" from website A for website B.
Generally speaking, "votes" from authoritative and relevant websites carry more weight.
There are many ways to get backlinks, and we focus on the most core and lowest-risk methods:
1. Get Others to Link to You Proactively (Earn Links)
This is the most ideal and most Google-encouraged way, which is not so "fast" but has the most lasting effect.
Core Actions: Create high-quality, uniquely valuable, and quotable content. This can be:
- A very useful free online tool or calculator.
- An in-depth industry research report containing exclusive data.
- An extremely detailed ultimate guide or tutorial that solves users' pain points.
- A novel point of view or a unique list of resources.
When your content is good enough, authors of other websites may discover your content and proactively link to it as a reference or recommendation when writing about related topics.
2. Add Some Links Yourself
This method is easier to operate, but the effect is limited, so do it moderately.
Core Actions:
- Industry directory: If your business has a physical or clear industry affiliation (such as a local business or software company), find several most well-known and authoritative industry vertical websites or business directories and submit your website information. For example, restaurants can submit to Yelp and TripAdvisor; software can submit to Capterra and G2, etc. (Only do the most important few!)
- Related communities/forums/Q&A: Occasionally in industry forums, online groups, Zhihu Q&A and other communities where you truly participate and are familiar, if the content of one of your web pages can really help answer a question or supplement a discussion, you can naturally leave a link. Never post spam advertising links in irrelevant communities! Doing so is likely to be deleted or even damage your reputation.
3. "Ask" for some links
Directly requesting links from other websites usually has a low success rate, because why should others help you? But there are a few relatively reasonable ways:
Core Actions:
- Guest blogging: This is a relatively effective method. You write a high-quality article for free for other relevant websites. In return, you can include one or two links to your own website in the author information or content of the article.
- How to do it (Simplified Version): Find some blogs that you think are good and related to your topic, and see if they accept submissions (usually there will be instructions on the website footer or contact page). Start by trying blogs that don't require high standards, and write an article that you are good at and that is valuable to their readers.
- Image Link Building: If original pictures or charts on your website are used by other websites, but they have not noted that you are the source, you can politely contact them and request that they add a link to your original picture page.
- Outreach email template: The
web.htmlfile does not provide an email template that can be copied and used directly. It also mentions that the success rate of sending emailsrequesting links blindly is very low. If you want to do guest blogging, you need to carefully write your submission instructions based on the style and requirements of the other party's website.
4. "Buy" links? Don't touch!
Core Warning: Ahrefs clearly states that buying links is not recommended.
- It is easy to buy junk links that are of no help to SEO and waste money.
- It violates Google's Webmaster Guidelines. Once discovered, your website may be penalized, leading to a significant drop in rankings or even removal from the index.
5. Maintain Your Existing Links
It would be a pity if the links you worked so hard to get were lost.
Core Actions: Check whether there are any pages on your website that cannot be opened (404 Not Found), but these pages had external links pointing to them before. Tool: Use the free Ahrefs Webmaster Tools. Steps:
- Log in to Ahrefs Webmaster Tools and verify your website.
- Enter the Site Explorer tool.
- In the left menu, select "Pages" -> "Best by links".
- Click the "HTTP code" filter and select "404 not found".
- View the report list. If you find a 404 page followed by a high "Referring domains" (indicating how many websites link to this page) number, it means that this invalid page used to be important.
- Find the new page URL on your website that is most relevant to the content of this invalid page (if there is no fully corresponding page, the homepage is also acceptable).
- Set up a 301 redirect to permanently redirect the URL of this 404 page to the new URL you found. In this way, the link value pointing to the old URL can be passed on to the new page. (How to set up a 301 redirect depends on your website server and platform, you may need to search for specific tutorials, such as "How to set up a 301 redirect in WordPress").
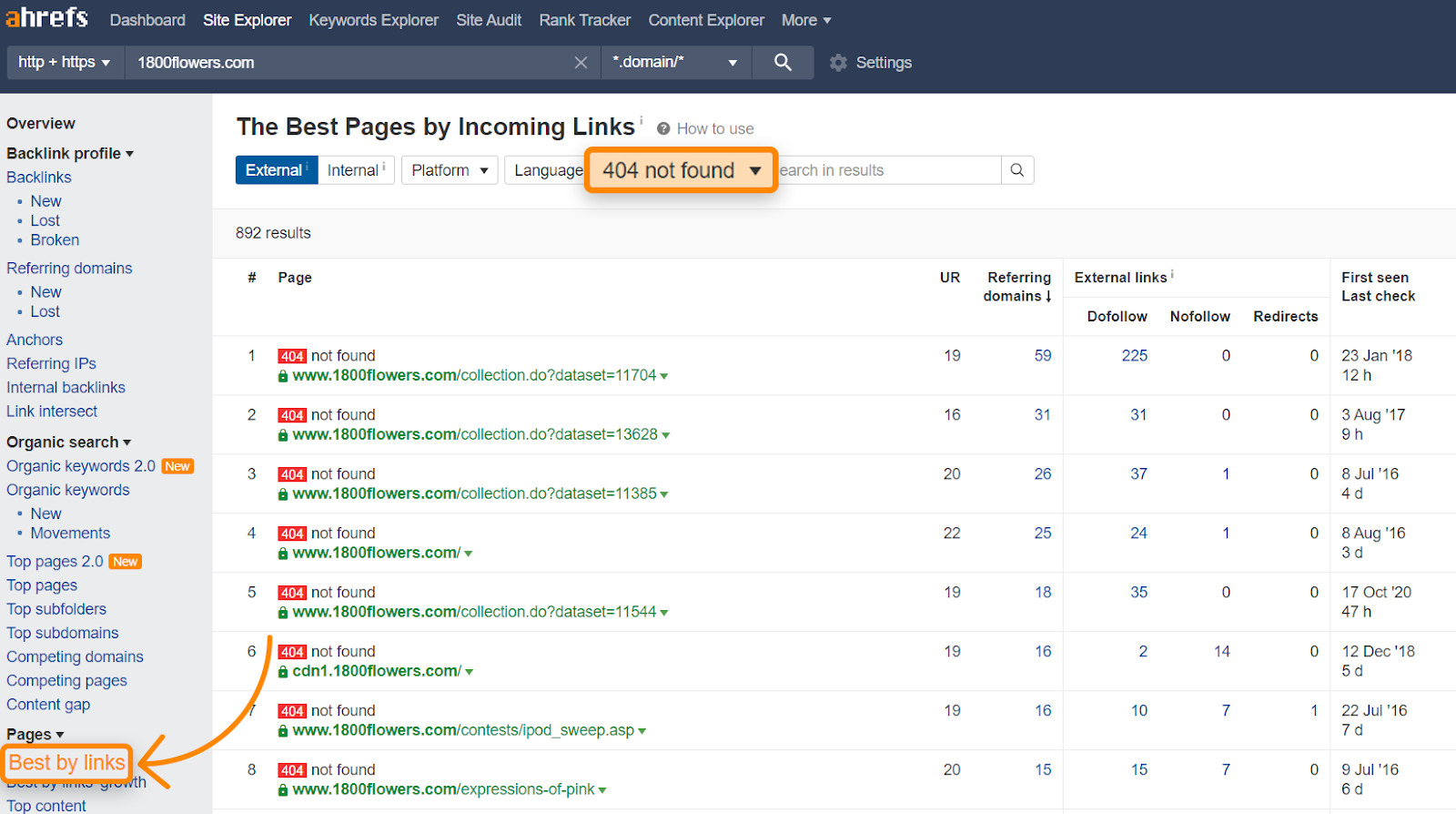 Image description: Using Ahrefs Site Explorer's Best by links report with a 404 filter to find invalid pages with external links (example from Ahrefs blog)
Image description: Using Ahrefs Site Explorer's Best by links report with a 404 filter to find invalid pages with external links (example from Ahrefs blog)
External Link Toolkit
Essential (Free):
- Ahrefs Webmaster Tools: View the links your own website receives, find 404 pages with links and fix them, and check the technical health of the website.
- Ahrefs Free Backlink Checker: Quickly view the top 100 external links of any website (including your competitors) to understand where they are getting links from.
- Google Alerts: Set up alerts related to your brand name, website name, and core themes. You will receive email notifications when new content related to these topics appears online. This helps you find cases where others have mentioned you but haven't added a link (you can request them to add it), or discover new link building opportunities.
5. Other Optimizations
- Check Indexing: Use the "URL Inspection" tool in Google Search Console (GSC, free) to ensure Google can find your important pages.
- Fix Broken Links: If you've changed URLs or deleted pages, use Ahrefs Webmaster Tools (AWT, free) to find pages that are now 404s but previously had external links. Redirect them to the new, relevant pages using 301 redirects.
- Adapt to Multiple Languages: If your niche is highly competitive, consider adapting your content to multiple languages. Many websites only compete in English, so translating your content can unlock more traffic.
- Create a Sitemap: Create a
sitemap.xmlfile listing all important pages on your website and submit it to Google Search Console. This helps Google discover your content faster and more comprehensively.- Example (Basic sitemap.xml Structure):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9"> <url> <loc>http://www.example.com/page1.html</loc> <lastmod>2024-01-01</lastmod> <changefreq>monthly</changefreq> <priority>0.8</priority> </url> <url> <loc>http://www.example.com/page2.html</loc> </url> </urlset>
- Example (Basic sitemap.xml Structure):
- Hreflang (Multilingual Tags): If your website has content in multiple languages or targeting different regions, use
hreflangtags to tell Google about the different language/regional versions of each page. This prevents duplicate content issues and ensures the correct version is shown to the right users.- Example (In HTML
<head>):
(Note:<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-us" href="http://www.example.com/en/page.html" /> <link rel="alternate" hreflang="zh-cn" href="http://www.example.com/zh/page.html" /> <link rel="alternate" hreflang="x-default" href="http://www.example.com/page.html" />x-defaultis used to specify the default or non-language-specific version)
- Example (In HTML
- Robots.txt (Crawler Instructions): Place a
robots.txtfile in your website's root directory to instruct search engine crawlers which pages or directories you don't want them to access or index (e.g., admin pages, test pages).- Example (robots.txt Content):
User-agent: * # Applies to all crawlers Disallow: /admin/ # Disallow access to /admin/ directory Disallow: /private.html # Disallow access to /private.html file Allow: /public/ # Explicitly allow access to /public/ directory (if a parent directory is disallowed) User-agent: Googlebot # Applies only to Google crawlers Disallow: /tmp/ # Disallow Google crawlers from accessing /tmp/ directory Sitemap: http://www.example.com/sitemap.xml # Specify Sitemap location
- Example (robots.txt Content):
- Canonical Tags: If your website has multiple pages with identical or very similar content (e.g., URLs with parameters), use
canonicaltags to specify which is the "official" version. This prevents search engines from treating them as duplicate content and diluting their ranking potential.- Example (In HTML
<head>):
(Note: Even on<link rel="canonical" href="http://www.example.com/product-page" />http://www.example.com/product-page?ref=bannerthis is page, point to the canonical URL without parameters)
- Example (In HTML
- Schema Markup (Structured Data): Add Schema markup to your page code to explain the meaning of the content to Google in a standardized format (e.g., this is a recipe, a product, an FAQ). This helps Google understand the content and may display richer snippets in search results (like ratings, price ranges, etc.), improving click-through rates.
- Example (JSON-LD Format, placed in a
<script>tag):{ "@context": "https://schema.org", "@type": "FAQPage", "mainEntity": [{ "@type": "Question", "name": "What is SEO?", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is the process of improving the ranking of a website in the organic search results of search engines (like Google) by optimizing its content and technical aspects." } },{ "@type": "Question", "name": "How long does SEO take to show results?", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "SEO's effects vary depending on website foundation, competition, and resources. Expect weeks to months or longer to see results." } }] }
- Example (JSON-LD Format, placed in a
6. SEO Tools
Free Tools
- Ahrefs Free Keyword Generator: Find keyword ideas.
- Ahrefs Webmaster Tools (AWT): Free site audits, keyword rank tracking, internal link opportunities, broken link checks, and more.
- Ahrefs Free Backlink Checker: Quickly view the top 100 backlinks to a website.
- Google Keyword Planner: Keyword research tool within Google Ads (requires a Google Ads account).
- Google Suggest: Autocomplete suggestions in the Google search bar.
- Google Related Searches: Related search terms at the bottom of Google search results pages.
- Answer The Public: Find questions and topics surrounding a keyword (has daily usage limits).
- Google Trends: View search popularity and trends for keywords.
- ChatGPT (Basic Version): Brainstorming, content generation, headline creation, and more.
- Google Search Console (GSC): Monitor website performance in Google Search, indexing status, technical issues, and more.
- TinyPNG / iLoveIMG: Online image compression tools.
- Google PageSpeed Insights: Test page loading speed and user experience.
- Schema Markup Generator (e.g., Schema.dev): Generate structured data code.
- Google Search Gallery: View supported Schema types and rich snippet examples.
- Google Mobile-Friendly Test: Test the mobile-friendliness of a webpage.
- Google Alerts: Monitor the web for new content mentioning specific keywords or brands.
- Next.js / Nuxt.js: Frontend frameworks that help build SEO-friendly websites.
- Industry Directories/Review Sites (Partially Free): Such as Yelp, TripAdvisor, can submit basic business information.
Paid Tools
- Ahrefs (Core Suite): Full-featured SEO tool platform, providing in-depth keyword research, competitor analysis, backlink analysis, website audits, and more.
- Semrush: Another full-featured SEO and marketing tool platform, with similar functionalities to Ahrefs.
- SimilarWeb: Another full-featured SEO and marketing tool platform, with similar functionalities to Ahrefs.
- Answer The Public (Paid Version): No usage limits.
- ChatGPT (Advanced Version): More powerful AI model.
- Industry Directories/Review Sites (Advanced Features/Advertising): Such as Capterra, G2, may offer paid promotion or advanced analytics features.
Finally
One last thing, I developed a tool, SparkNow, to help you start projects in one stop, SEO detection, external links, performance, publicity texts, publicity pictures, are all done for you, with a large amount of guaranteed, interested friends can try it, if you are not interested, just ignore it, mastering the above SEO methods is enough.